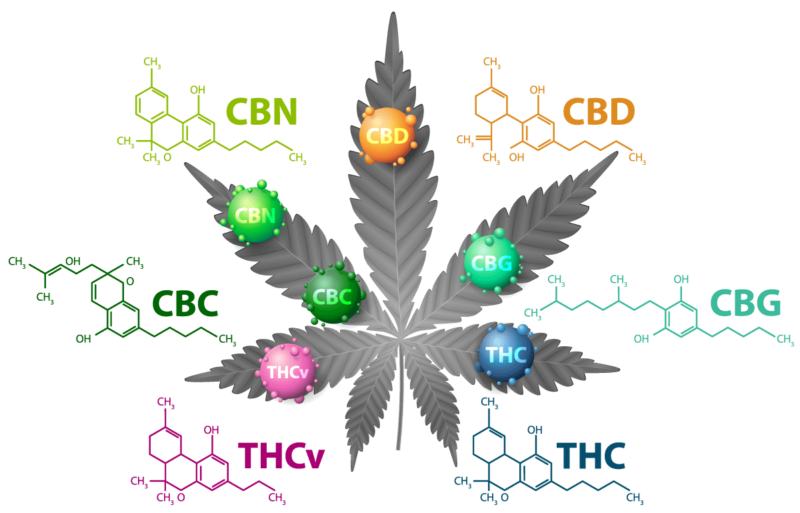
What are cannabinoids and cannabis?
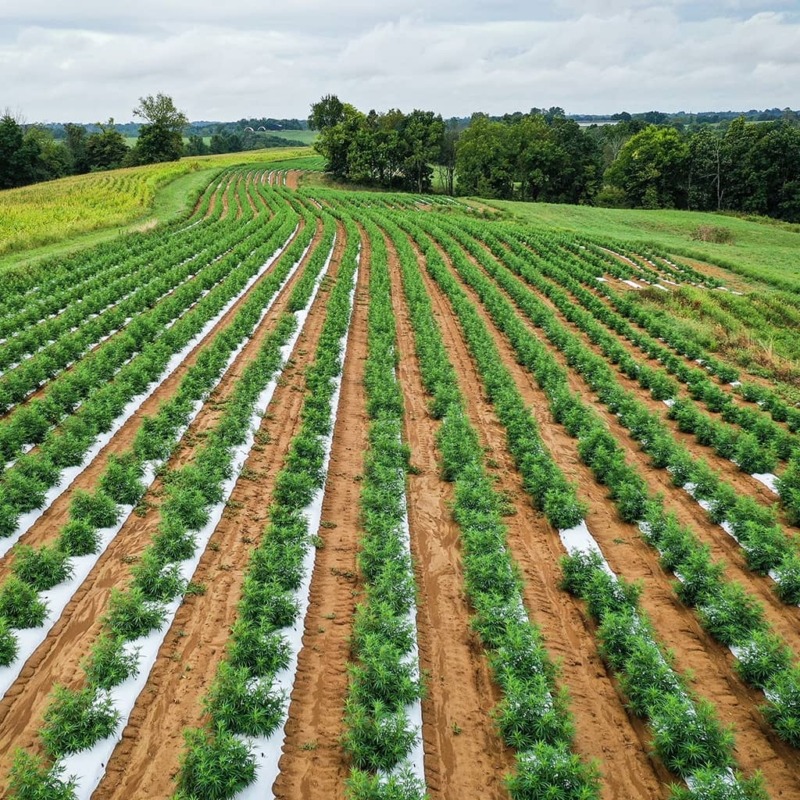
Cannabis, much like other versatile plants like corn and potatoes, can be selectively bred and cultivated for diverse applications. Regardless of its intended purpose, the cannabis plant inherently contains a myriad of cannabinoids – naturally occurring compounds that have become the focal point of extensive deliberation, research, and scholarly inquiry. Irrespective of regulatory categorization as ‘hemp’ or ‘cannabis,’ the cannabis plant serves as the primary source of these cannabinoids. The genesis of cannabinoids commences with a singular molecular compound known as cannabigerol (CBG). As the cannabis plant matures in its natural environment, CBG undergoes natural conversions into cannabidiol (CBD), Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and more than 150 other cannabinoids.
THC, scientifically denoted as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, constitutes one cannabinoid, and so does CBD. Given its psychoactive properties, cannabis with a THC content exceeding 0.3% is subject to varying degrees of regulation in the United States, encompassing adult recreational use, medicinal usage, or outright prohibition. In contrast, CBD, along with non-intoxicating cannabinoids like CBG and CBN, is integrated into a wide array of unregulated products, readily accessible at grocery stores and day spas alike.
Our comprehension of the cannabis plant and its constituent cannabinoids is constantly expanding. As the nation progresses towards broader legalization and the regulation of recreational intoxicants, informed and empowered consumers will have access to a spectrum of legal, regulated THC-based products. In this context, regulatory bodies play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and quality of these products.